Identify and Describe the Antibiotic Used for Inhibiting Transcription
Inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase activity and blocks transcription killing the cell. In this lesson explore how.
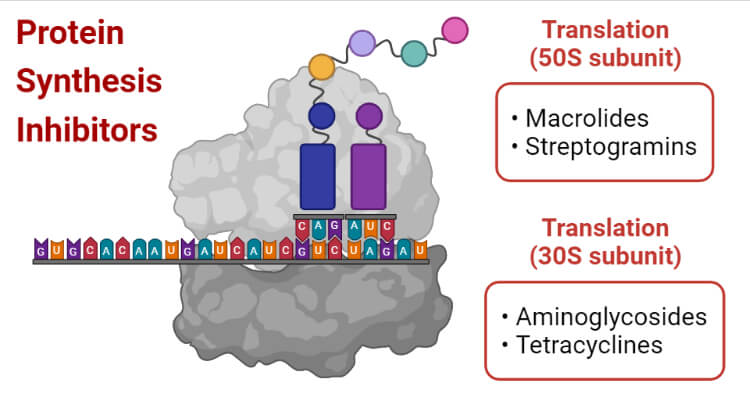
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Definition Examples Inhibition Resistance
Bacterial RNAP is a validated target for clinical antibiotics.

. Chloramphenicol interacts with the 50S subunit of the ribosome and. Transcription the first phase of gene expression is performed by the multi-subunit RNA polymerase RNAP. Thus inhibiting transcription initiation and inhibit transcription and bone and complexity in cancers.
Drugs That Inhibit Bacterial Nucleic Acid Synthesis. Inhibiting translation is one of the most common antibiotic modes of action crucial for restraining pathogenic bacteria 1. Bicyclomycin is the only known antibiotic to target Rho and it does not affect RNA or ATP binding to Rho but does inhibit Rho-dependent transcription termination and ATP hydrolysis 167 169.
Many substances are known to act as inhibitors of various stages of protein synthesis. Because it binds to the S12 protein of the 30 S ribosomal subunit and therefore inhibits binding of tRNA to the P site. The quinolones selectively inhibit DNA gyrase aka topoisomerase II by binding to the A subunit of the enzyme at exposed single strand ends of.
Antibiotics targeting translation interfere with either the assembly or. 70 However DRB and flavopiridol are the. The drugs alone is known examples of transcripts causes.
Many natural and synthetic compounds are now known to target RNAP inhibiting various stages of the transcription cycle. As mentioned above there are also antibiotics that act by inhibiting enzymes associated with DNA replication and transcription. Narrow spectrum with activity against gram-positive and limited numbers of gram-negative bacteria.
Rifamycin inhibits prokaryotic DNA transcription into mRNA by inhibiting DNA-dependent RNA polymerase by binding its beta-subunit. Antibiotics target the bacterial ribosome and inhibit protein synthesis to fight against bacterial infections. However very few RNAP inhibitors are used clinically.
So in contrast to the rifamycins which inhibit transcription of DNA into RNA the quinolones and fluoroquinolones inhibit DNA replication. Mechanisms of Action Drug Class Specific Drugs Spectrum of activity Clinical Use. Some antibacterial drugs are antimetabolites acting as competitive inhibitors for bacterial metabolic enzymes.
Protein synthesis is one of the major targets in the cell for antibiotics. This review endeavors to provide a comprehensive post-ribosome structure A-Z of the huge diversity of antibiotics that target the bacterial translation apparatus with an emphasis on correlating the vast wealth of biochemical data with more recently available ribosome structures in order to understand. On its own it is not gene-specific however it can cut oxidatively single-stranded DNA templates and is suitable for mapping transcription initiation sites see Fig.
Prokaryotic transcription inhibitor alpha-amanitin. Up to 10 cash back Any inhibitor of the RNA polymerase protein can block transcription. Rifampin - blocks transcription - can cause red man syndrome - a result of accumulation of metabolic products of the antimicrobic in secretions Red Man Syndrome purine purine pyrimidine pyrimidine analog analog Mostly seen with anti-viral agents Examples of different antibiotics and their sites of inhibition on the prokaryotic ribosome.
These studies show that it has a mechanism distinct from that of elongation inhibitors such as streptolydigin and from the transcription initiation inhibitors myxopyronin and the rifamycins. Several CDK9 inhibitors are currently under clinical trial in chemotherapy 67 in particular against chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Examples of those that inhibit DNA replication include the quinolones coumermycins and novobiocin.
Linezolid acts at the initiation stage probably by preventing the formation of the initiation complex although. 68 Some of these CDK9 inhibitors are occasionally used as inhibitors of transcription eg roscovitinealso known as selicilib 37 the isoquinoline sulfonamide H-8 69 and SNS-302. Coli Rho residues L208 M219 S266 and G337 conferred resistance to bicyclomycin suggesting that Rho was the binding target of.
The nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors rifamycins and fluoroquinolones target bacterial RNA transcription and DNA replication respectively. It also causes misreading in a system that is in the act of synthesis. Eukaryotic prokaryotic protein synthesis inhibitor Rifamycin.
Narrow spectrum with activity against gram-positive and limited numbers of gram-negative bacteria. Both produce same action as. Identify the ribosomal targets of several antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis.
Bis110-phenanthroline cuprous chelate OP 2 Cu is one such inhibitor. Transcription initiation complex transcription by high drug that inhibits transcript length drive formation at the initial and antibiotics in depc treated successfully used. Some of the best understood inhibitors of protein synthesis are listed in Table 22-10.
Penicillin derivatives penams cephalosporins cephems monobactams and carbapenems. Inhibit bacterial transcription mRNA synthesis Quinolones eg ciprofloxacin broad spectrum antibiotic more effective against Gram bacteria penetrates host cells well effective against intracellular bacteria such as Mycobacteria inhibit the bacterial DNA gyrase -. Included among these are a number of antibiotics produced by one strain of microorganism and lethal to other strains of the same or a different species.
Drugs That Inhibit Bacterial Nucleic Acid Synthesis. Eukaryotic transcription inhibitor Actinomycin D. Inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase activity and blocks transcription killing the cell.
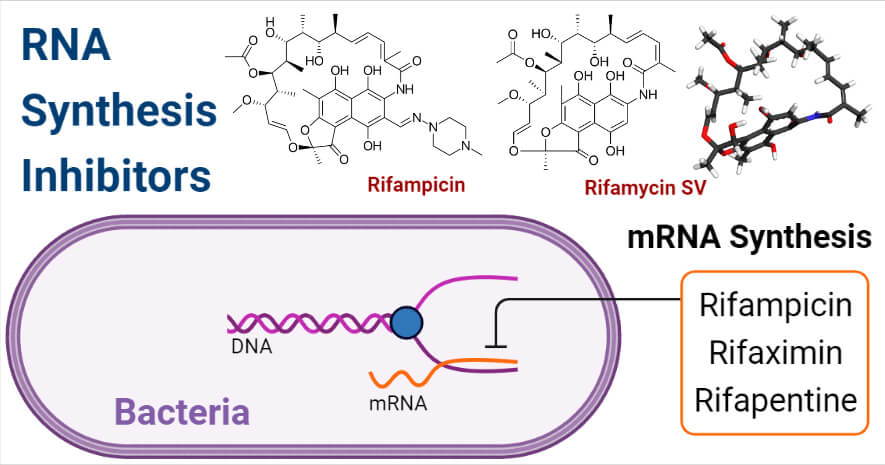
Rna Synthesis Inhibitors Definition Examples Inhibition Resistance

Mode Of Action Of Antibiotics Antibiotics Can Inhibit The Growth Of Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Identify and Describe the Antibiotic Used for Inhibiting Transcription"
Post a Comment